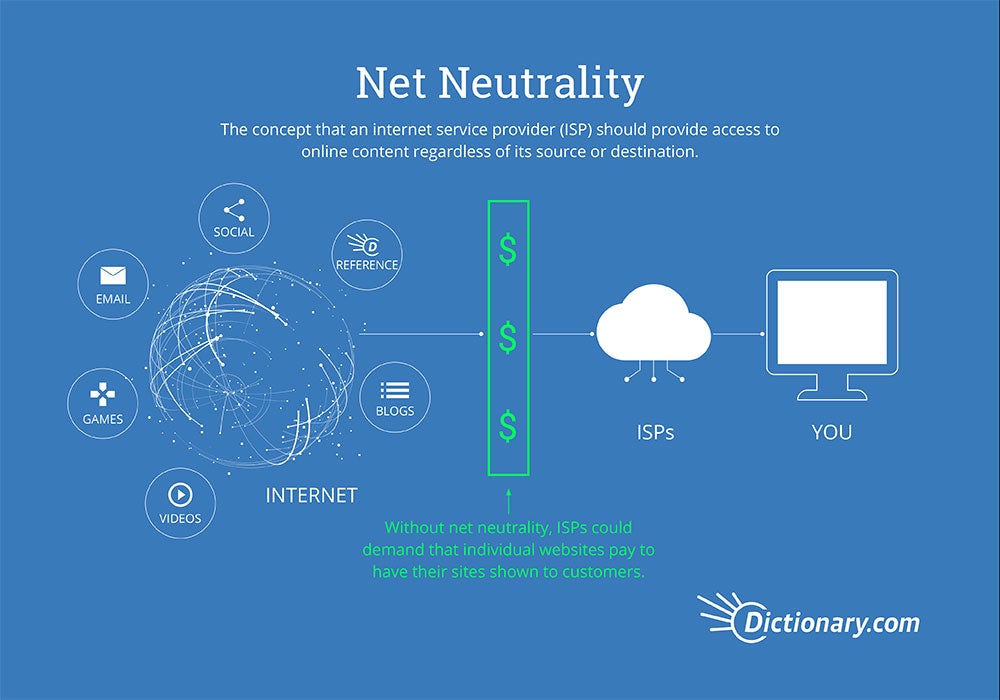
What is Net Neutrality?
Net neutrality is a priciple that all data that is on the internet must be treated equally by internet service providers and governments, regardless of user, content, site, platform, equipment or method of communication. This means that service providers and the government cannot slow down or block content from users of the internet. Net neutrality laws protect internet freedom by requiring internet service providers to provide the same level of data access and internet speeds.