
What is Internet Censorship?
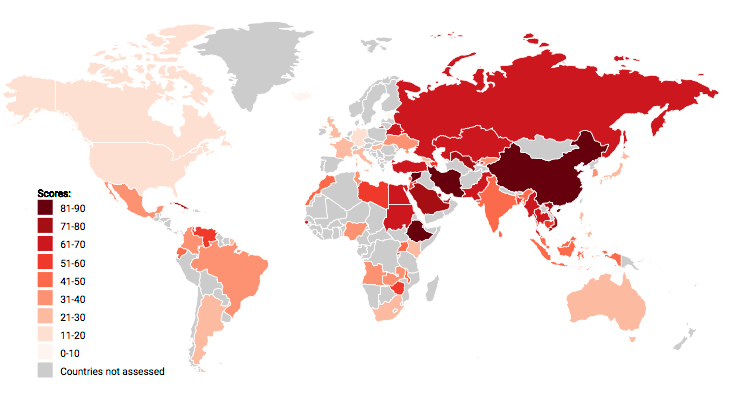
Internet censorship is the suppression and control of information online and access to the internet. This is performed by regulatory institutions, usually government entities or large corporations. Internet censorship can occur for a number of reasons, and can be a constant thing, or used in emergency situations. Internet censorship varies by nation, with certain nations such as the Democratic Republic of Korea and Iran being considered more restrictive. Internet censorship affects access to information on the internet, with certain sites or data on specific topics being hidden. Internet censorship is not internet content moderation, for internet censorship applies to government action to control information, while website owners have a right to remove comments on their site they deem inappropriate.
How does Internet Censorship Work?
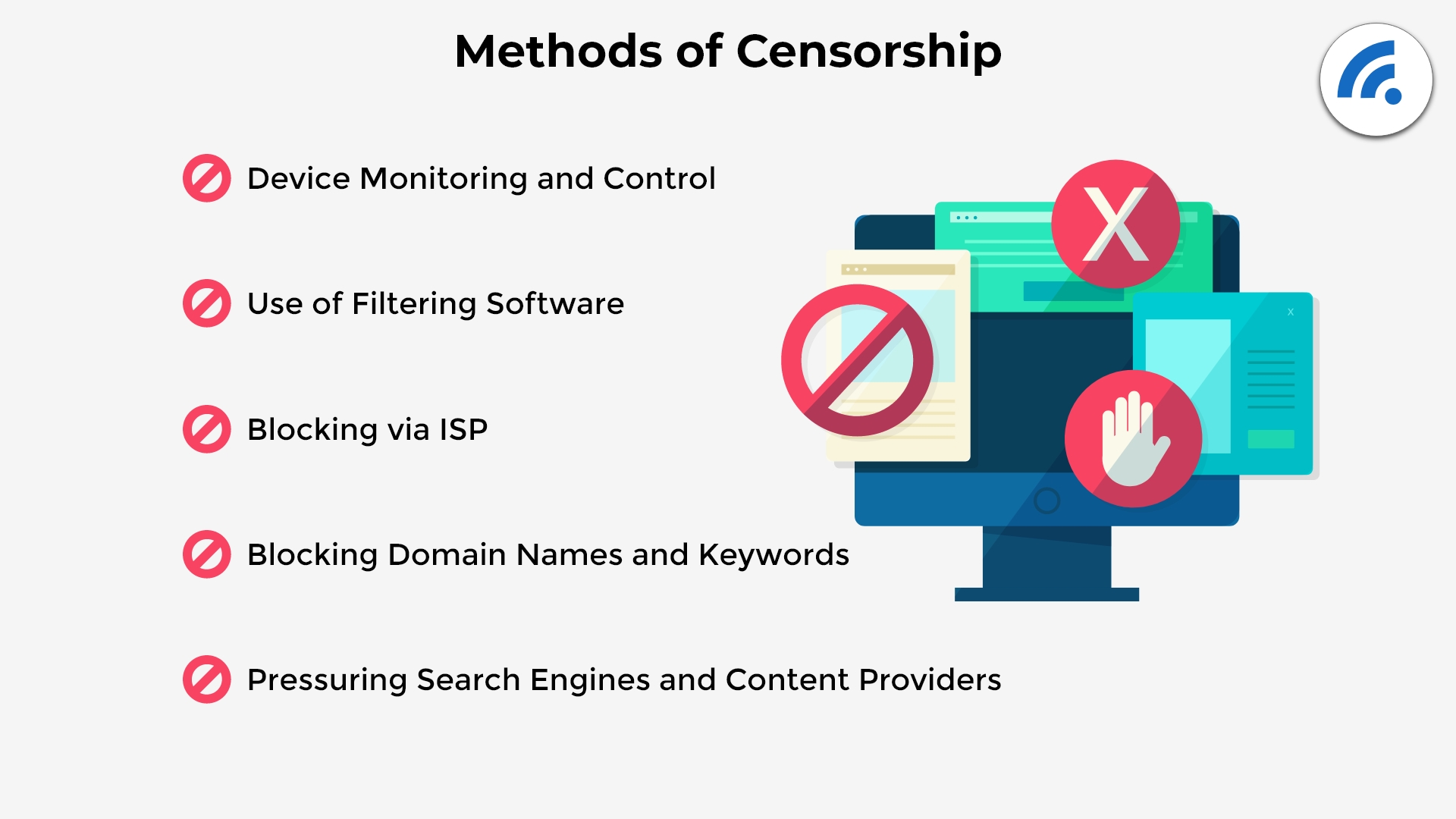
Governments censor internet information through a number of tactics. One tactic is the use of software to filter and block access to certain websites, which is especially common on public devices. Some countries have power over internet service providing companies, or search engines. By having control over these companies, governments can force companies into taking down websites, or manipulating internet search results. This affects access to information for everyday internet users living in these countries. Other avenues for internet censorship include blocking domain names, blocking keywords in searches and, in more extreme cases, partial control over the manufacturing of computer devices.
Impact of Internet Censorship
Internet censorship normally regulates inappropriate or violent content, as well as sensitve government information and political news deemed unsatisfactory by governing bodies. Nations such as China promote internet censorship by pressuring internet service provider companies into regulating their clients. Internet censorship allows certain groups to control access to information, as well as push certain narratives. This can hinder the ability of average consumers and citizens to freely access information. It can also allow governments to hide dangerous or classified information, and monitor internet activity, protecting their citizens.